Initials from Choir Books
These initials belonged to a magnificent set of liturgical manuscripts which were among the finest art works created in Florence during the decades around 1400. They combine the monumentality of panel paintings with the exquisite delicacy of manuscript illumination.
The Choir Books from which these initials came were illuminated between 1370 and 1506 by successive generations of artists. They were made at the Camaldolese monastery of Santa Maria degli Angeli, the leading intellectual and artistic centre in Florence c. 1400. Its scriptorium produced sumptuous manuscripts for religious houses in Tuscany and the Veneto as well as for its own community. The Camaldolese monks sang out of these Choir Books while celebrating religious feasts. The volumes, mutilated during the Napoleonic invasion of Italy (1797-1809), are still in Florence (Biblioteca Laurenziana, Corali 1-19). The initials, which were excised from them and sold on the art market, are now dispersed in public and private collections across the globe. These four initials graced the pages of the earliest volumes, produced from 1370 onwards.
Learn more about these initials by exploring the sections below or selecting one of the images on the right. Discover further details by choosing any of the images, where you can view the hotspots by clicking on ![]() .
.
The initials depicting the Presentation in the Temple and St Clement are among the earliest works of Don Silvestro dei Gherarducci, dating to the 1370s. By the 1390s, he was the most distinguished Florentine illuminator and after his death in 1399, his right hand was venerated as a relic. The other two initials have been attributed to various artists.
The Choir Books to which three (and perhaps all four) of these initials belonged were made for the use of the Camaldolese monks at Santa Maria degli Angeli between 1370 and c.1450.
During the Napoleonic invasion of Italy (1797-1809), the initials were cut out of the volumes which remain in Florence (Biblioteca Laurenziana, Corali 1-19). Marlay cutting It. 13A and MS 5-1979 were fol. 42 and fol. 159 respectively in Corale 2. Marlay cutting It. 13.i was fol. 62 in Corale 19. Marlay cutting It. 13.ii might have been fol. 19 in Corale 3 or may have belonged to another, lost set of Choir Books illuminated in Florence between 1373 and 1382.
Subsequently, Marlay cutting It. 13A belonged to Sir Samuel Meyrick (1783-1848), while Marlay cuttings It. 13.i and It. 13.ii were at the Museo Cavaleri in Milan. All three were bequeathed to the Fitzwilliam Museum in 1912 by Charles Brinsley Marlay (1831-1912).
MS 5-1979, which had belonged to Joseph Henry Fitzhenry (1836-1913) and Sir Thomas Ralph Merton (1888-1969), was purchased by the Fitzwilliam Museum in 1979.
The historiated initials marked the start of texts chanted by the Camaldolese monks at religious feasts throughout the year. They came from two types of Choir Books, Graduals and Antiphoners, which contained the sung parts of the Mass and the Office respectively. The letters belonged to the opening word of the text sung on each feast – the Introit to the Mass in Graduals and the responsory or antiphon for the relevant office in Antiphoners.
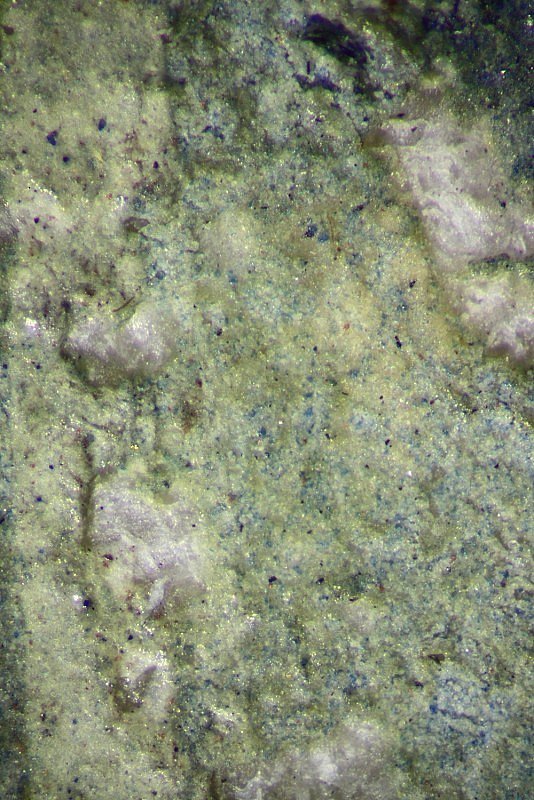
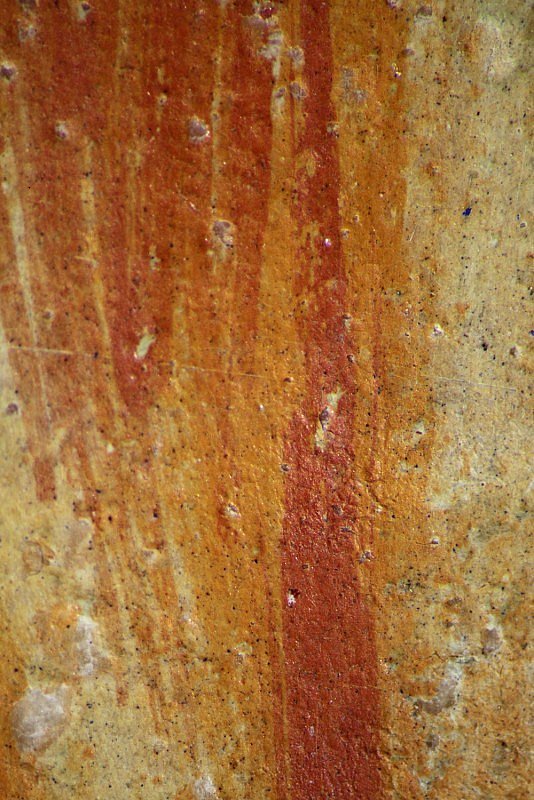
The range of pigments used to paint these four initials is remarkably similar. Some differences can, however, be observed, as may be expected for works painted over four decades. The common pigments include carbon black, lead white (used on its own and mixed with other pigments to modify their hue), vermilion, red lead, ultramarine blue, organic pinks and mosaic gold. Green hues were obtained by mixing azurite blue with two different yellow pigments. Gold leaf was laid over a ground containing gypsum and a red bole, and burnished to a high shine. Egg yolk was used as a binder in some areas of each initial.
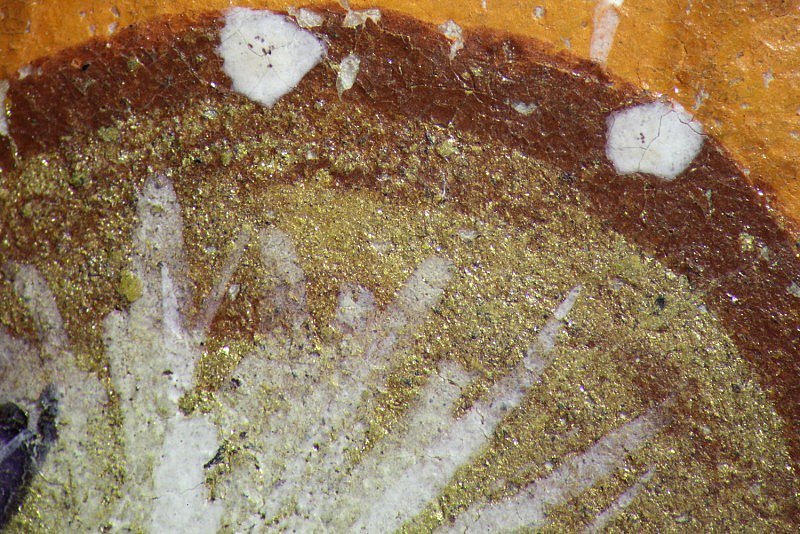



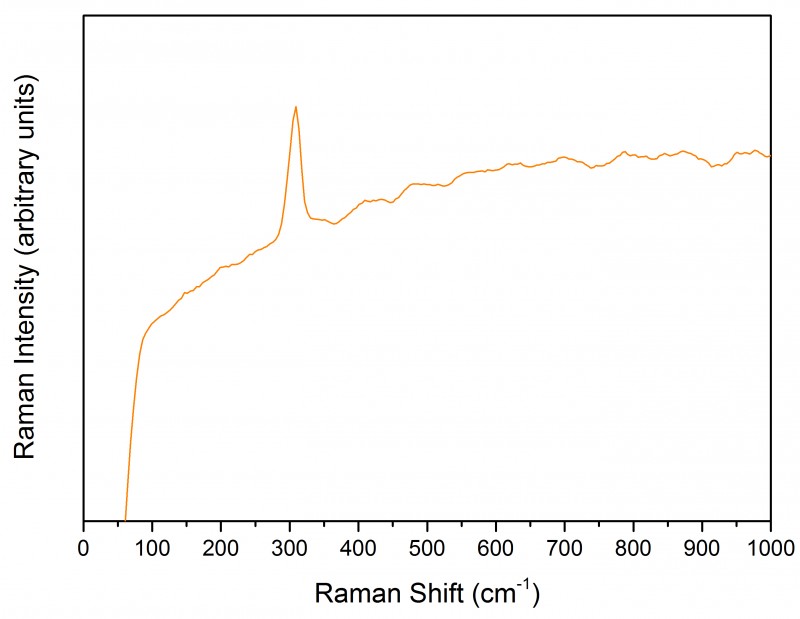
Detail of
the mosaic gold leaf, outlined with a dark red earth pigment, under
magnification (16x). Its shiny aspect and the characteristic peak at 308 cm-1
in the Raman spectrum (below) confirm the presence of mosaic gold.
St Laurence
Historiated initial L from an Antiphoner, 1390s
The initial L belonged to the office of Matins for the feast of St Laurence (10 August) in Corale 19, an Antiphoner made in the 1390s. St Laurence is shown with a book, a martyr’s palm branch and his distinctive attribute, the gridiron on which he was tortured. The image has been attributed to various artists: Don Silvestro dei Gherarducci; his collaborator known as the Maestro delle Canzoni; or the Florentine painter and illuminator Mariotto di Nardo.
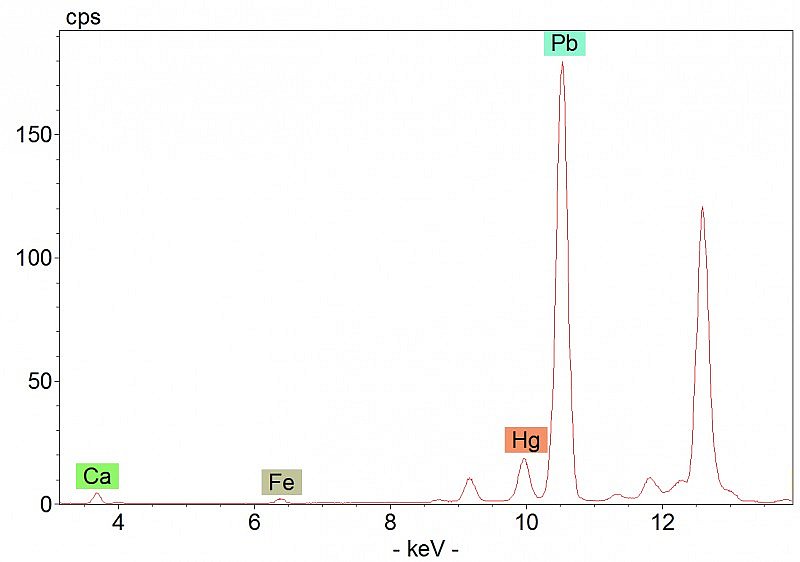
It is also possible that the figure of St Laurence and the decorated initial were painted by two different artists; despite general similarities, some differences exist between the pigments used in these two areas. Green hues, for example, were all obtained using a mixture of azurite with a yellow pigment. The palm leaf held by the Saint, however, seems to contain ultramarine as well (hotspot 1). The XRF data also suggest the presence of gypsum in most of the border areas analysed, but not in the figure of the Saint.
Related content: Initials from Choir Books
- Artists: The Artists associated with the initial of St Laurence
- Texts and Images: St Laurence
- Description and Contents: Physical Description
- Description and Contents: Script and Textual Contents
- Artists' Materials: Differences in palette
- Artists' Materials: Selective use of egg yolk binder
- Artists' Techniques: Gold tooling
- Artists' Techniques: Painting the flesh
